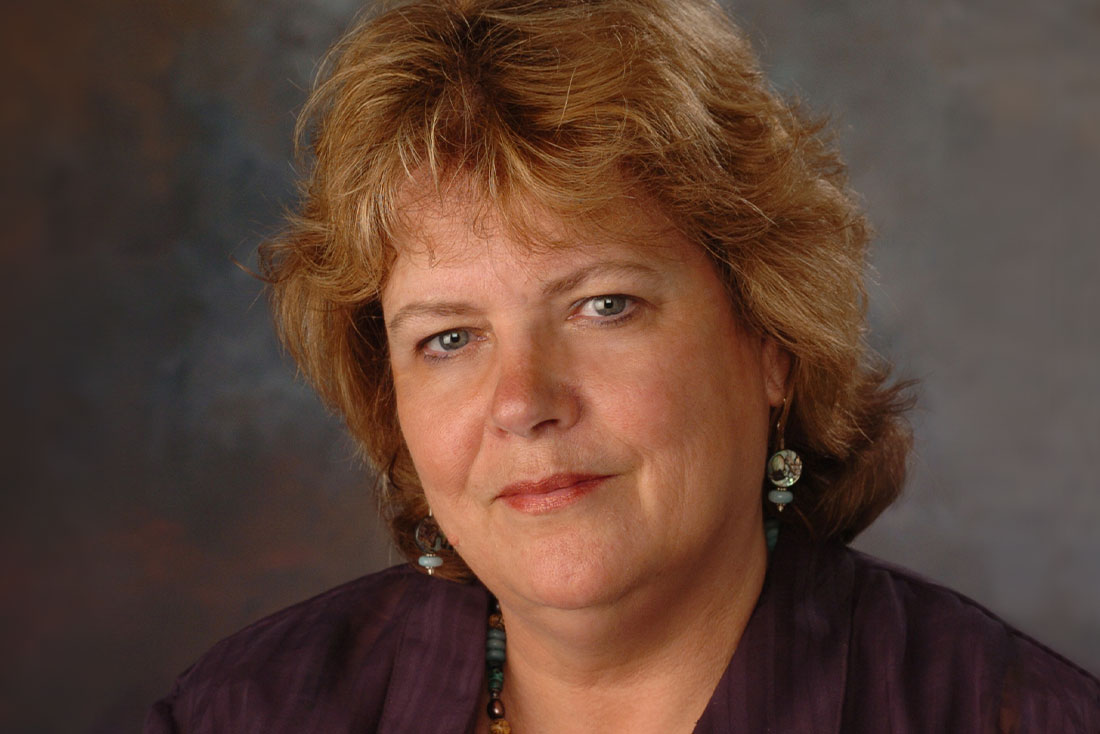

Many know Diane Lyden Murphy as the Dean of Falk College, a position she has held since 2005. But her journey and impact at Syracuse extend well beyond her deanship. In many ways, her leadership in Falk College was shaped by the people and experiences in Diane’s life before Falk College even existed.
As we approach the end of August 2023 and the conclusion of her deanship, we sat down with Diane to reflect on her personal journey to academia; her calling to social policy, social justice, and feminist scholarship; and her remarkable 45 years of service at Syracuse University. Here is her story:
Moving In a Crowd
“Do you want to be a jumping hyena? Or do you want to play ball?” One of the sisters who taught at Our Lady of the Valley, a Catholic high school in Orange, New Jersey, was encouraging a young Diane Lyden to join the basketball team. It was the early 1960s, a time when women’s competitive sports were still new and most young women were cheerleaders. “The nuns were my first feminist teachers,” she said. “I didn’t know it then.”
Thanks to the nuns’ encouragement, Diane joined the women’s team, which won several state championships in northern New Jersey. “I wasn’t top of the team. But my very best friend Bernie was. She was a top shooter in Jersey. Boys would get scholarships every year. But there were no scholarships for Bernie, so she did not go to college.”
Growing up in North Jersey, there were Irish, Italian, and Polish neighborhoods. At home, she was part of a multi-generational household of first-generation Irish Catholics. Diane was the eldest of 10 children—four girls and six boys. The house was huge, and it needed to be—it was home to her siblings, grandparents, and aunt and uncle “I’ve always lived in a gang, that’s how I moved around and knew life. There were always little kids around. There was always lots of activity. We went to school, and church, and athletics. You had to do well in your own role.”
In school and at home, Diane found a mix of “old world” culture mixed with the social justice values of her Jesuit education and home upbringing. “The whole ethos and modeling and life I had was always built around issues of social justice and giving back and philanthropy, mutual aid, and leadership in that area. The concept that what you’re given must be returned,” she said.
The family went to mass every day, and they all worked by the time they were 16. “I either volunteered, or by 16 I had a job.” In high school, Diane was a hospital volunteer, often called a “candy striper.” Even there, Diane was marching to her own drum. “I kept getting into trouble because I kept on serving the people. You’re supposed to just give them their food and leave—but I kept on feeding the old people,” she said, grinning. “The nurses finally said to me, ‘You’re only supposed to leave the trays, you’re not doing the right job, you’re fired,’” she laughed. “I had a little rebel streak. If anybody said don’t, I did.”
But as traditional and new ideas of the world in the 1960s found themselves at odds, Diane found a way to preserve the best of both and still push for progress. Perhaps her biggest act of individual thinking was her decision to go to college. Diane had a knack for academia; she took three years of math, and even won a state award for her four years of Latin language education.
Although she was at a college prep school, her family did not understand why she wanted to go to college. No one in her family had earned a bachelor’s degree, and the women didn’t receive any college education. Money for higher education was reserved for the men in the family. Her father, an Irish biological orphan raised by an adoptive Polish family, had an associate degree and a stable white-collar job in traffic control. Just as Diane was finishing high school, her father was being transferred to Upstate New York. Since her family was relocating to Syracuse, Diane enrolled at Syracuse University.
A Born Social Worker
Diane became part of the progressive action movement in the community and on campus. “It was a social activist time. It completely meshed with my own mission and values. So, I became an activist scholar.” She majored in sociology at the Maxwell School and was part of the honors program. At the time, social work was not an undergraduate major.
“My parents didn’t help me financially because they couldn’t. I always worked. I worked at the bookstore, lifeguarding, water safety. I worked all through college. I did my schoolwork at home at night.” As an undergraduate student, Diane lived with her family in a big farmhouse. She shared a room with her two sisters. Second in birth order was Diane’s sister, who was following a more traditional path. And while her grandmother gave her sister a dowry, Diane only wanted books. “Grandma would say, ‘Any money I give you will not go into a book!’ It was so far from her experience as a farm child in the Catskills.”
As a senior, she received her honors degree in Hendricks Chapel. “My parents came for the first time to campus, and my father said, ‘What are you doing?’ Meaning, ‘What is this all about?’ My family always loved me and supported me, but, having never experienced it themselves, did not understand higher education.” Although her family did not understand Diane’s chosen path, she credits them with setting her on it. “My inclination to social justice comes out of my early preparation as a child. My parents showed the way,” she said. “All my brothers and sisters do this work. We’re all involved in human services: Doctors, healthcare workers, lawyers, social workers, teachers, and on and on it goes.”
While at Syracuse, Diane met Fred Murphy, a graduate student in economics at the Maxwell School, five years her senior. “He was also an activist scholar. He was employed by the City of Syracuse doing tenant organizing.” One week after her graduation in 1967, Diane and Fred were married. In January 1969, their twin daughters were born.
No Stopping Her
Diane was working at Elmcrest Children Center with a team of six women, each of whom had their Master of Social Work. “You’re a born social worker,” her supervisor told Diane. After a year at Elmcrest, she made her way back to Syracuse to earn her own M.S.W.
Diane arrived at the admissions office with her twins and was greeted with a comment she’d never forget: “‘What are you doing with those babies sitting in my office for admissions?’ he said to me. ‘I’m applying to graduate school.’ ‘And what makes you think that’s reasonable, young lady?’ I said, ‘Because women do it all.’ I was so upset, it got me charged up. I said to myself, ‘I’m really going to do this!’”
She started courses in social work in the fall of 1969. “By this time there was no stopping me. I really loved my studies in social work.” At the time, her twins were not yet 1 year old. There were no childcare services on campus for students with children, and since Fred was working full time, they went to class with Diane. “I took them to school. I brought them to class,” she said. “Still to this day my friends from graduate school talk to me about holding them on their lap. I often rode on a bike with them—one on the front and one on the back. It was a little challenging, but all my friends I met in class helped me do it.” In the M.S.W. program Diane became president of the social work Graduate Student Organization.

Diane paid for her education through scholarships and teaching assistant stipends. These turned into formative experiences for her. “I was given the opportunity to make family-friendly structural changes for all members of the university community, working side-by-side with mentors, university leaders, and countless collaborators.”
In her first year as a graduate student intern, Diane worked with Central New York Legal Services in local family court cases. In her second year, she worked with Dr. Charles Willie, then-Dean of Student Affairs and previous chair of the sociology department whose research focused on mental health in African American families. “That was an unbelievable adventure working with him as his graduate assistant. What a privilege. He ended up being tenured at Harvard University’s School of Education. Under his mentorship, we developed and founded the Syracuse University Early Childhood Education Center.”
By the early 1970s, there was a large population of married students and families, many of whom were having children. But there were only minimal health benefits at Syracuse University. The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) was more than 20 years away. “Dr. Willie said to me, ‘Married students are a poverty population.’ And they were.” And although Syracuse University had the Bernice M. Wright Laboratory School, the school was a cooperative model, and it didn’t take infants. Together, Dr. Willie and Diane as his graduate assistant established the Early Childhood Education Center funded between the Department of Psychology, the School of Education, and the Office of Student Affairs. They also created a program with SUNY Upstate Medical University to help students access affordable childbirth delivery.
After completing her M.A. social science in 1976 and her M.S.W. in 1978, Diane decided to continue with a Ph.D. “Obviously I was kind of pushing against things all along, and now it became pretty obvious what the mission was. There’s no question of the intentional effort that we would make this university a model for family friendly policy.”

Trained by the Very Best
Throughout her doctoral studies, Diane worked with Dean of the School of Education Burton Blatt, Doug Biklen, Bob Bogdan, Steve Taylor, and other scholars and partners at the Center on Human Policy in the School of Education. “These were the School of Education’s flagship signature moments, and we were the literal pipeline of funding from Washington. Most of the federal funding for the nation came to Syracuse University for disability studies.” In part, the Center worked on deinstitutionalization and the promotion of community care models. “This was a big part of my journey in my 30s and 40s and this movement in disability studies transformed America,” she said.
Diane’s colleagues at the Center were trailblazers for inclusive education. The Jowonio School was an early pilot of inclusive education modeling that was created by the School of Education. They integrated these models into the Early Childhood Education Center and the Bernice M. Wright Laboratory School before they became the model for the surrounding Syracuse community, and eventually the world. “Now inclusive education is mainstream. Syracuse University School of Education built that,” she said. “I am pleased to say every one of my children have been educated within an inclusive education environment. It makes a world of difference, and everyone benefits.”
All of Diane’s doctoral work was done with the Center on Human Policy. In her graduate assistant office on campus, she kept a crib for the twins where they would sleep while she wrote her dissertation.
She earned her Ph.D. in 1983 and by then, Syracuse University was truly her home. “I had a lot of good fortune,” she said. “I had been trained by the very best and got to do the work I love, which is organizing and planning social change, having the university engage in the community and the community engage in Syracuse University.” She loved academia, and she felt part of the community. And perhaps most importantly, she could see an opportunity to make change in the place she had grown to call home. “I realized I could do activist organizing within the university community and make this a better place for all,” she said. “So, I stayed, and I never left.”
Together You Create the Shift
As a member of the University Senate since 1979, Diane was deeply involved in writing new policies for the university. She and her colleagues formed policies for women’s concerns, gender pay equity, and sexual harassment. They established benefits for parental leave, adoption, domestic partnerships, and retirement. “We looked across the nation and even in Europe to see what best healthcare policies to have at a university. We adapted them, we brought them in, we pushed for them. You have to be strategic and skilled in community change and movement and organization theory—and we were. So, we’ve attended to all those things and we’re a better place because of it.
“But we can’t rest on this,” she continued. “Although there has been accomplishment, we realize there is a harsh political context to consistently work in. But the university has been responsive through its legislative and statute process, through the University Senate, our chancellors, and our provosts, and community leaders have been responsive to working towards a progressive site. That’s a gain for the entire community.”
Active in the early women’s movement in the wider community, Diane was one of four charter members of The Women’s Center, which operated consciousness raising (or “CR”) groups in Syracuse and surrounding towns. It’s still active and located on Allen Street and Harvard Place. From 1993-1994, Diane served alongside her colleague Dr. Marie Provine, a lawyer and Chair of the Department of Political Science, as consultants to Chancellor Kenneth Shaw on women’s issues.
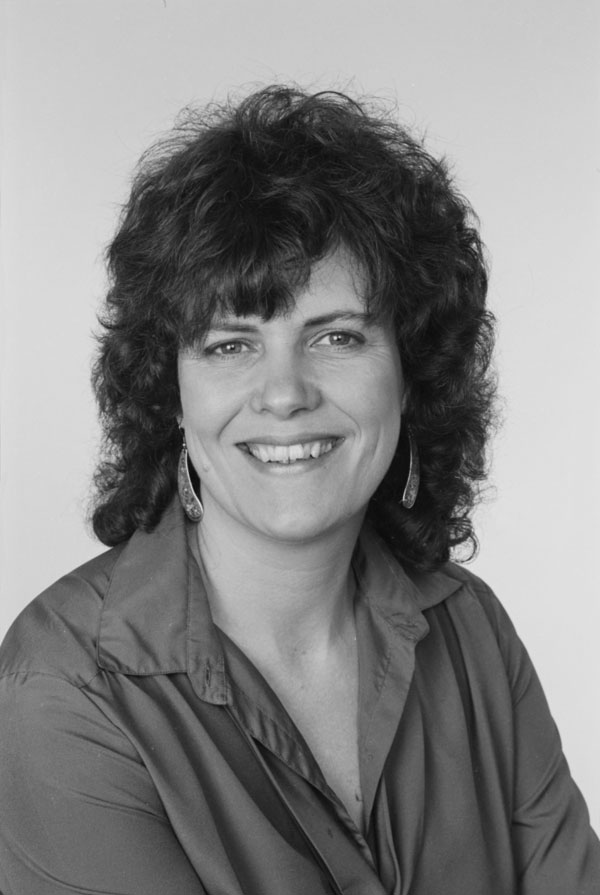

In 1989, Diane took on a new role establishing women’s studies at Syracuse University. She recalls university leadership asking, “Why do we need women’s studies?” “Because everything else is men’s studies,” she said. She was Director of Women’s Studies for more than 16 years. Together with her colleagues, they established women’s studies as a department in the College of Arts and Sciences, and created a major, a minor, and a certificate of advanced study. “Women’s studies is an articulation of giving women the opportunity to study every subject through the lens of women and their history and contributions. It shifts the perspective by focusing on women in all academic fields. And it has created the movement of women’s perspective entering every field of knowledge without exception. This perspective is not yet universal, and there is more progress to be made,” she said.
“You do that collectively,” she continued. “Collectively means you have women that are interested in doing this and leading this as mentors in every possible place in the university and community, and together you create the shift in knowledge.”
Following Dr. Claire Rudolph and Dr. Nancy Mudrick, Diane in 1978 became the third female faculty member to join the School of Social Work. She taught macro policy and law in mental health and developmental disability policy, emphasizing the importance of building change into structures, processes, and systems. “I know as an organizer, until you build it into the structure, it goes with the wind.” She loved teaching her students how to work with people to make progress–something she’s been doing her whole life. But perhaps her biggest challenge was yet to come.
We’re Going to Build It
In 2001, Syracuse University merged the College for Human Development, the School of Social Work, and College of Nursing together to form the new College of Human Services and Health Professions (renamed the College of Human Ecology in 2007), led by Dean William Pollard, former Dean of the School of Social Work. The merge raised questions from faculty about the future of their programs. What does it mean for the formerly independent disciplines? How would the programs continue as a collective College? “It was a challenging time,” said Diane.
In the fragile early years of transition, the university began a search for Pollard’s successor. Although a dozen candidates were vying for the job, Diane wasn’t one of them. But the university leadership identified her as a strong candidate, thanks to her track record of success in leadership and community organizing. She was heavily recruited. Still, many of the university’s leaders openly expressed their doubts about the ability of the college to succeed. She recalls a conversation with one member of university leadership who said, “If I were you, I would take the job and let it fall to its own because it’s never going to work. Let it fall apart and that’ll be the end of it.”
Even Diane had her doubts. But taking the job under the assumption of failure was unacceptable to her. She would accept the job under only one vision: that it would succeed. “I remember saying to myself, ‘If I’m going to do this, we’re going to do it! If these schools must be arranged like this, then we’re going to build it so that we can live and thrive in this structure. Otherwise, all the programs will go away.’ And that’s what I said to the committee: We’re going to build this thing.” In 2005, she was selected unanimously by full faculty vote.

For Diane, failure wasn’t an option. The programs themselves—professional programs in health, nutrition, social work, human development, and others—were too vitally important to society in promoting health and equity. “I said to the faculty, ‘We’re going to take this College and make it what we want it to be. What we know it is. But we will do it. We won’t let it fail because our subject matters are too important. We can do this together—and we will do this together.’”
Diane was the perfect choice to join people together to create a new community. “I was raised in a crowd from the time I was a young person in a large family. I move in a crowd.
“I never make decision alone,” she continued. “I assume that I have other experts around me—we bounce off ideas, we have discussions, and we come to collective work that I think represents the best of everyone. And that’s guided me even to the deanship.”
As the College structure was being formed, so was its identity. With Diane at the helm, the college was built on the principles of social justice and civic engagement. It became a college where putting theory into practice is about more than just gaining practical experience, but about serving others and fostering humility and understanding in diverse global cultural contexts.
Among the merged colleges was a curriculum for sport management, written by faculty in consumer studies, one of the academic programs that had been newly introduced as part of the merge in 2001. In 2004, Falk College launched sport management built on the framework of social justice and corporate social responsibility. In many ways, a socially minded business program was ahead of its time. But the students embraced it, and since 2006 they have raised more than half a million dollars for local charities and continue to lead discussions about diversity and equity in sports.
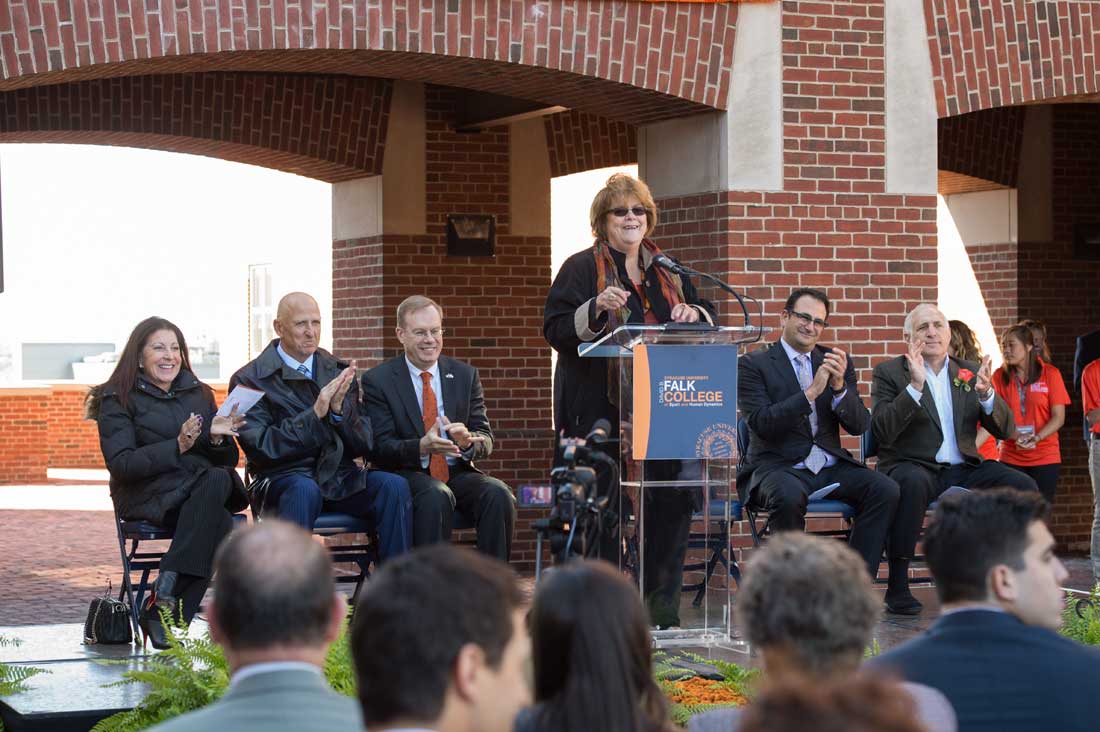

With support from Syracuse University alumni David Falk ’72 and Rhonda Falk ’74, the College was renamed the David B. Falk College of Sport and Human Dynamics in 2011. The Falk College Complex, former home of the College of Law, was dedicated 2015. Falk programs which had been dispersed in eight different locations across campus were finally all together under one roof. “It’s 18 years since I became Dean, and we have built it. We are a huge success on every dimension,” she said. “We’ve done it as a collective. We’ve done it as a community.”
Today, Falk College boasts impactful interdisciplinary faculty research in human services, health, and social equity. The curriculum integrates highly effective theory-to-practice learning models for student training. Falk College created new undergraduate and graduate academic programs in food studies, esports, and sport analytics at Syracuse University, new programs public health from the legacy of the former College of Nursing, and new programs in exercise science which began in the School of Education. Students also benefit from new global study abroad programming across Europe, Asia, and Africa.
But most importantly, every year the College graduates a cohort of students who are prepared to make their communities stronger, healthier, and more just places. “When students come and study in Falk College, they’ve already made decisions about what they want to do in their life. They want to be largely involved in improving the lives of others through their professional career. They bring such joy, commitment, eagerness, and innovation. That’s the everyday lift you get from being around Falk students.”

Accomplishment in Doing Good
Diane recalls words from a colleague and friend who said to her, “I have never seen anybody fight so hard and forget so easy. You can work with anybody.” She has grown to be admired for her ability speak truth to power in a way that maintains respect and preserves unity.
“I have an ungainly and probably not grounded sense of self confidence, and still do to this day,” admitted Diane, a self-described “straight-shooter.” But she is still inclined toward a bit of humor. Empathy and humility have been guiding principles in her life and leadership. “I don’t feel above anybody else, and I always value diverse perspectives,” she said.
For the campus community, Diane’s legacy will be her effectiveness as an advocate for change and her ability to move groups of people together for better. “It’s a sweet and lovely feeling of accomplishment in doing good.”
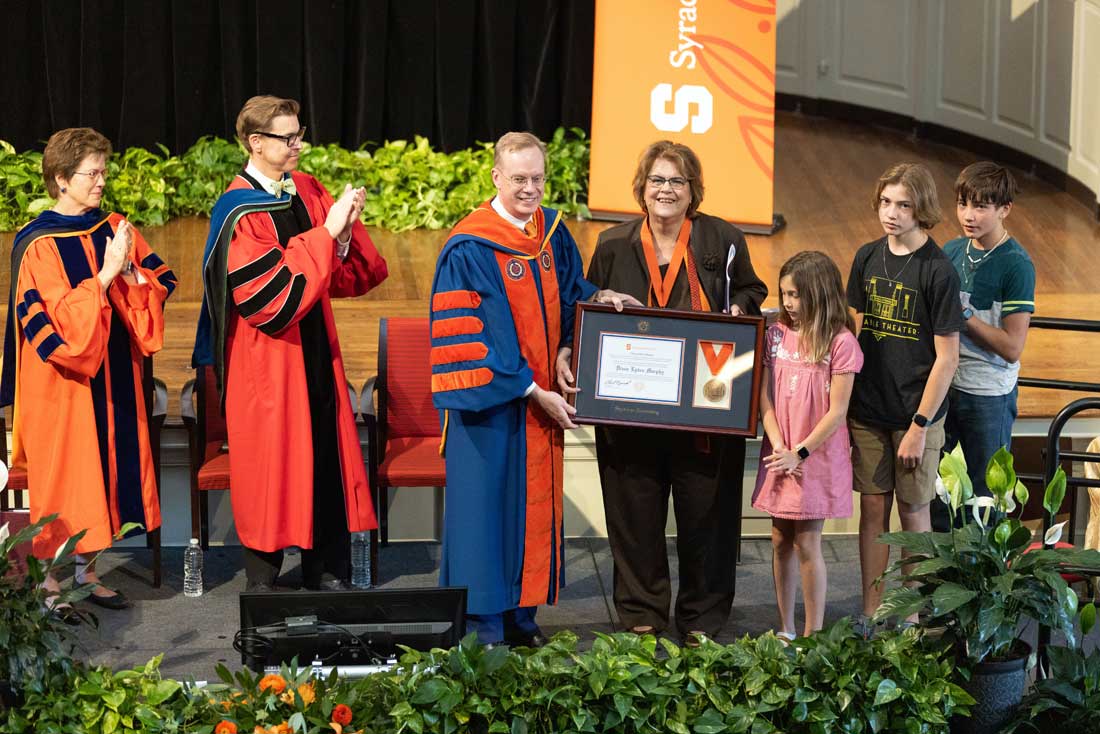

But for Diane, her legacy is the one she shares with her late husband, Fred: Their five daughters, their grandchildren, and their commitment to their communities. “I am certainly a feminist. I get it right back at me now from five feminist daughters of whom I am immensely proud.” All her daughters work in education, health, and helping professions. All are heavily involved in civic activity, and not by accident “Fred and I raised our family in the City of Syracuse by determination. We’re urbanists.” Still today, Diane is a proud member of the Westcott community.
Over the years, Diane’s big family home just kept getting bigger, encompassing her family, her Syracuse neighbors, and the university community. “I feel privileged to have had the chance to practice my own values, my own mission, my own journey as I saw it with my family. To be able to execute that and to live that life comfortably and bring that to work, I mean, what an opportunity. I get to work every day at what I love to do. It is quite a privilege and I know that.”
Thanks to Diane and the progress she helped forge in favor of social justice, more people can enjoy that same privilege of shaping their own path in life and living out their own personal mission in all circles of influence–at home, at work, and in the community–instead of having to choose. After all, if Diane has demonstrated one consistent truth, it’s that change can only be achieved if it is achieved together.
Story by Valerie Pietra. Special thanks to Matt Michael for editorial collaboration and contributions and Syracuse University Archives Special Collections Research Center for research and photography.
